
More Allergy, Asthma & Infectious Disease Articles
Exploring the Various Types of Eczema and Their Unique Symptoms
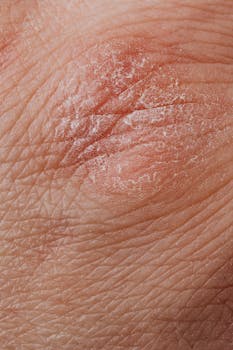
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects people all over the world. Understanding the different types of eczema is essential for proper management and care. Each type comes with its own set of symptoms and triggers, making recognition crucial for effective treatment.
Different Types of Eczema
Eczema is not a one-size-fits-all condition. Below, we will explore several forms of eczema, shedding light on their unique characteristics, common triggers, and treatment options. Understanding these differences can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema, often starting in childhood but can occur at any age. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. The condition is often linked to genetic predispositions and other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
People with atopic dermatitis may experience flare-ups due to environmental factors such as pollen exposure, weather changes, and certain foods. Moisturizers and topical steroids are typically used for management, but exploring holistic wellness approaches to support overall health can also be beneficial.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. There are two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. The former is caused by repeated exposure to a substance, while the latter results from an immune reaction to an allergen.
Typical symptoms include redness, itching, and blisters. Avoiding known triggers and using barrier creams can help mitigate symptoms. Patch testing can be a valuable tool in identifying culprits.
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema presents as small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet. Triggers often include stress, prolonged exposure to moisture, and metal exposure from jewelry. This type of eczema can be chronic and may require dermatological intervention when severe.
Management strategies include keeping the hands and feet dry and using cold compresses to alleviate itching. Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to control inflammation.
Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema is identified by round, coin-shaped spots that are itchy and inflamed. Unlike other types of eczema, nummular eczema often occurs after a skin injury, such as a burn or insect bite, and can last for weeks or even months.
This type of eczema is managed with moisturizers and topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. Avoidance of harsh soaps and irritants can also help prevent flare-ups.
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis is primarily seen in older adults and is caused by poor blood circulation, typically in the lower legs. It leads to swelling, redness, and itchy skin. Long-term cases may result in more severe complications like ulcers.
Compression stockings and elevating the legs can help improve circulation, while emollients keep the skin moisturized. Medical advice is often necessary for this condition to prevent complications and manage symptoms effectively.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis affects areas of the body with many oil-producing glands, like the scalp, back, and face. It appears as scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff.
This type of eczema can flare up due to stress, cold weather, or hormonal changes. Treatments include antifungal shampoos, corticosteroids, and creams that contain calcineurin inhibitors.
Effective Management of Eczema Symptoms
While understanding the different types of eczema is a critical first step, effective management often involves a combination of therapies personalized to individual needs. Emphasizing healthy skin care routines, identifying triggers, and seeking professional advice are fundamental strategies.
Keeping abreast of new research and treatments is beneficial. For a global perspective on health conditions, you can explore resources such as those provided by Wikipedia.
In conclusion, managing the different types of eczema requires a comprehensive approach that includes both prevention and treatment strategies aimed at reducing symptoms and enhancing the quality of life.
- Eczema encompasses a variety of types, each with distinct symptoms and triggers.
- Proper identification and management strategies are essential for minimizing flare-ups.
- Moisturizers, topical treatments, and lifestyle modifications play key roles in care.
- Nutritional and holistic approaches may support skin health and overall wellness.
- Consulting with healthcare providers ensures customized treatment plans.
FAQs
What is the most common type of eczema?
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema, often occurring in children but also affecting adults.
Can eczema be cured?
There is currently no cure for eczema, but various treatments can effectively manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups.
How can one prevent eczema flare-ups?
Preventing eczema flare-ups involves avoiding known triggers, maintaining a regular moisturizing routine, and using prescribed medications as directed.
Are natural remedies effective for eczema?
Natural remedies may complement traditional treatments, but it’s essential to consult healthcare providers before trying new approaches to ensure safety and efficacy.
Is it necessary to see a doctor for eczema?
Yes, consulting a dermatologist or healthcare provider is important for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Other Articles You May Find of Interest...
- Effective Relief Options for Upper Respiratory Issues with OTC Medications
- Is Macrobid a Sulfa Drug or Not? Discover the Truth About Your Antibiotics
- Is Zyrtec Safe to Use During Pregnancy?
- Can Prednisone Help Treat Pneumonia Effectively?
- Bronchitis or Pneumonia: How to Identify the Key Differences for Better Health
- Managing Reactive Airway Disease: What the ICD-10 Code Means for Your Health
- Exploring the Impact of Gram Negative Diplococci on Human Health














