
More Vascular Health Articles
Why Is My Hematoma Lump Not Healing?
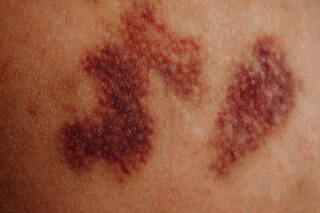
Dealing with a hematoma lump that won’t go away can be frustrating and concerning. A hematoma, which is essentially a collection of blood outside of blood vessels, typically arises from some form of trauma or injury. While most hematomas heal over time, there are instances when they linger longer than expected. This article explores possible reasons, treatment options, and when to seek medical advice.
What is a Hematoma?
A hematoma forms when blood vessels are damaged, causing blood to leak into surrounding tissues. This can result in swelling, discoloration, and a noticeable lump or mass. Hematomas can occur in any part of the body, including muscles, skin, or the brain. The size and severity of a hematoma can vary significantly depending on the injury’s location and impact.
Why a Hematoma Lump Won’t Go Away
There are several reasons why a hematoma lump might persist. In some cases, the body may have difficulty reabsorbing the blood, particularly if the hematoma is large. Poor circulation, certain medications, and underlying health conditions such as bleeding disorders may also contribute to delayed healing. Additionally, repeated trauma or pressure to the area can hinder recovery.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can influence the development and persistence of a hematoma:
- Injury: Physical trauma from sports, falls, or accidents can cause blood vessels to rupture, leading to a hematoma.
- Medications: Blood thinners and other medications that affect clotting may prolong the healing process.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like hemophilia, liver disease, or vitamin deficiency can impair clotting and healing.
If you frequently notice unexplained bruising or hematomas, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any serious conditions. For more information on addressing underlying health issues, consider learning how a functional medicine doctor addresses root causes.
Treatment Options for Persistent Hematomas
If your hematoma is not healing, several approaches may help:
- Rest: Allowing the body to heal by resting the affected area is essential.
- Ice: Applying ice for 15-20 minutes at a time can reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Using a bandage to compress the area can help control swelling.
- Elevation: Keeping the affected area elevated above the heart can decrease blood pooling and promote absorption.
In some cases, further medical treatment may be necessary, such as draining the hematoma or taking medications to manage pain and inflammation.
When to See a Doctor
While many hematomas resolve on their own, certain signs indicate a need for medical intervention. If you experience severe pain, significant swelling, or if the hematoma shows no signs of improvement after two weeks, consult a healthcare provider. Additionally, seek immediate medical assistance if you display symptoms of infection, such as redness, warmth, or fever.
External Resources
For more in-depth information on hematomas and their treatment, visit Wikipedia’s entry on hematomas.
Final Thoughts
Understanding why a hematoma lump won’t go away can help you take appropriate steps toward recovery. Persistent hematomas typically require a combination of rest, home care, and sometimes medical intervention. Be sure to monitor your symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for advice tailored to your specific situation.
- A hematoma forms due to blood leaking from vessels into surrounding tissues.
- Various factors, including medications and health conditions, can impede healing.
- Home remedies like rest, ice, compression, and elevation can aid recovery.
- Seek medical help if the hematoma persists beyond two weeks or shows infection signs.
- Consult healthcare providers for persistent or concerning hematomas.
What causes a hematoma?
A hematoma is caused by injury to blood vessels, leading to blood pooling. Trauma from falls, impacts, or surgery can trigger it.
How long should a hematoma last?
Small hematomas often resolve within a week or two, while larger ones may take several weeks to months to heal completely.
Can medications affect hematoma healing?
Yes, medications such as blood thinners can prolong the healing process by impairing clotting and preventing the body from effectively reabsorbing blood.
Is massaging a hematoma advisable?
Generally, massaging should be avoided, particularly in the early stages, as it might spread the blood further and increase discomfort.
When is surgical intervention necessary for a hematoma?
Surgical drainage might be necessary if a hematoma is large, painful, or causing significant pressure on surrounding tissues.
Other Articles You May Find of Interest...
- Are There Hidden Dangers in Nattokinase Side Effects?
- Can Blood Thinners Help Reduce Blood Pressure?
- Why Is My Hematoma Lump Not Healing?
- Navigating Life After Triple Bypass Heart Surgery: Essential Tips for Recovery
- What Your Clubbed Nails Might Reveal About Your Health
- Recognizing and Responding to Shock and Haemorrhage Emergencies
- What Do Black Fingernail Lines Mean for Your Health?














