
Your Health Magazine
4201 Northview Drive
Suite #102
Bowie, MD 20716
301-805-6805

More Health News & Research Articles
Beyond Milligrams: Why Bioavailability Defines Efficacy in Cardiovascular, Cognitive, and Inflammatory Health
This article was written by: MVS Pharma GmbH’s team of medical/pharmaceutical experts: Riya Jayapal Roja – Senior Pharmacist & Dr Disha Trivedi – PhD in Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology
Introduction
Traditionally, the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries have equated efficacy with dosage, operating under the assumption that higher milligram amounts produce stronger clinical effects. While this straightforward model has facilitated product development and prescribing practices, it fails to account for a key pharmacological principle: bioavailability is often a more decisive factor in therapeutic effectiveness than the sheer quantity administered. The benefits of a compound—whether aimed at improving cardiovascular health, supporting cognitive function, or reducing inflammation—depend on how much of the active ingredient is absorbed, survives metabolic processes, enters systemic circulation, and reaches the intended site of action in a biologically active form.
As scientific understanding of pharmacokinetics deepens, the conversation around efficacy is shifting. Increasingly, researchers and healthcare professionals are focusing on absorption efficiency, metabolic transformation, and targeted delivery rather than relying solely on dose-based metrics. This evolving perspective highlights the importance of formulating interventions that prioritize bioavailability as a core determinant of clinical impact.
In pharmacology, therapeutic efficacy is not determined solely by the amount of a compound consumed, but by its ADME profile—absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. If a compound is poorly absorbed, rapidly metabolized, or inefficiently distributed, it is unlikely to reach therapeutic concentrations at the target site, regardless of the dose administered. This challenge is well illustrated by compounds such as curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids, and various nootropic agents. Despite encouraging preclinical findings, numerous clinical trials have failed to demonstrate efficacy due to formulations that did not adequately address bioavailability. Such outcomes underscore the inseparability of pharmacokinetics and therapeutic performance.
Bioavailability in Cardiovascular Health
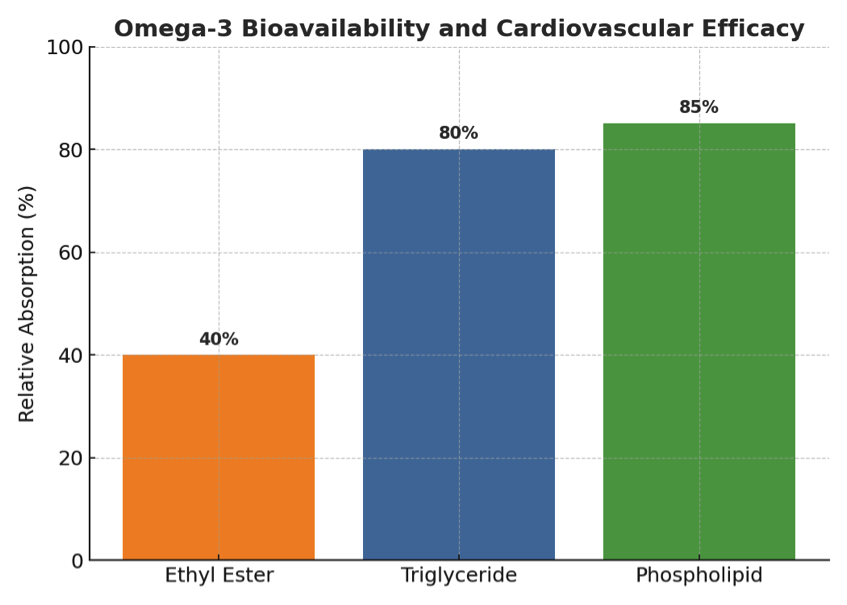
Omega-3 fatty acids, most notably eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are widely recognized for their cardioprotective roles. They help lower triglyceride concentrations, stabilize cardiac cell membranes, reduce platelet aggregation, and give rise to specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) such as resolvins and protectins that actively modulate vascular inflammation. However, the true clinical benefit of omega-3 supplementation cannot be gauged by milligram dosage alone. Bioavailability is the decisive factor in determining efficacy.
- Formulation: Ethyl ester omega-3s demonstrate lower absorption compared to re-esterified triglyceride or phospholipid-bound forms. As a result, two products both labelled “1000 mg fish oil” may lead to very different plasma EPA/DHA concentrations.
- Absorption Context: Because omega-3s are fat-soluble, their uptake is significantly enhanced when taken with dietary fats. In contrast, consumption on an empty stomach reduces absorption, limiting their therapeutic value despite equivalent doses.
- Metabolic Transformation: The cardiovascular benefits of omega-3s rely heavily on their enzymatic conversion into SPMs. Without adequate systemic availability, these downstream anti-inflammatory and lipid-regulating effects remain muted.
In cardiovascular care, efficacy is therefore not defined by capsule size or label claims, but by the proportion of EPA and DHA that successfully enter circulation in an active form and reach vascular targets. For clinicians, this underscores the importance of selecting formulations and strategies that optimize absorption and metabolic utilization, rather than focusing solely on nominal dosage.
* This image was generated with AI
The Concept of Bioavailability in Cognitive Health
Omega-3 fatty acids —most notably docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—are indispensable for preserving cognitive performance. DHA serves as a fundamental structural element of neuronal membranes, where it enhances membrane fluidity, supports synaptic plasticity, and regulates neurotransmitter function. It also contributes to neurogenesis and helps mitigate oxidative stress within the brain. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), although less concentrated in neural tissue, provides complementary benefits through its anti-inflammatory effects and influence on mood regulation.
Despite these well-established roles, the cognitive impact of omega-3 supplementation cannot be assessed solely by the number of milligrams consumed. Bioavailability ultimately determines whether these fatty acids reach the brain in physiologically meaningful amounts.
- Gastrointestinal Absorption – Compounds must withstand digestive processes and be effectively absorbed through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream.
- Metabolic Transformation – Following absorption, many substances undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can either enhance their biological activity or diminish it.
- Systemic Distribution and Transport – Once in circulation, compounds must remain stable, exhibit adequate solubility, and be efficiently transported to target tissues.
- Passage Across the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) – Only molecules with specific properties—such as lipid solubility, low molecular weight, or compatibility with active transport mechanisms—can cross the BBB and access brain tissue.
- Cellular Uptake and Functional Integration – Within the brain, compounds must be taken up by neurons, glial cells, or endothelial cells to influence neurotransmitter activity, oxidative balance, or the structural integrity of neural networks.
Examples
- Curcumin: Despite gram-level doses, plasma concentrations remain low, and CNS penetration is minimal. Bioavailability-enhanced formulations (liposomal curcumin, curcumin + piperine) demonstrate improved effects on cognition.
- Flavonoids (Blueberry, Green Tea): Their cognitive benefits rely on metabolites that cross the BBB and modulate neuronal signalling and cerebral blood flow.
- Omega-3 DHA: Critical for neuronal membrane fluidity, yet bioavailability depends on dietary context and enzymatic conversion.
Bioavailability in Inflammatory Health
Inflammation is a central driver of cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic dysfunction.
Many bioactive compounds with proven anti-inflammatory potential—such as polyphenols, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and curcumin—have shown inconsistent results in clinical trials. A key reason is that dosage expressed only in milligrams overlooks the critical role of absorption and systemic availability.
Examples
- Curcumin and Inflammatory Mediators: Conventional curcumin exhibits poor systemic absorption, which restricts its capacity to influence NF-κB signaling and cytokine activity. Bioavailability-enhanced formulations, however, demonstrate significant reductions in biomarkers such as CRP and IL-6.
- Vitamin D: As a fat-soluble vitamin, its immunomodulatory efficacy relies on efficient lipid transport and enzymatic conversion to active forms.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Their anti-inflammatory effects, mediated through specialized pro-resolving mediators like resolvins and protectins, are determined not by sheer intake but by the extent to which these metabolites are bioavailable.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are key modulators of inflammatory pathways. They act as precursors to specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs)—including resolvins, protectins, and maresins—that actively resolve inflammation and facilitate tissue healing. Through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, and by influencing immune cell activity, omega-3s help mitigate the chronic, low-grade inflammation that drives cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, autoimmune conditions, and metabolic disorders.
* This image was generated with AI
Professional Perspective: Clinical and Formulation Considerations
For experts in the pharmaceutical and medical fields, moving from a milligram-focused approach to a bioavailability-centred framework carries significant implications:
- Clinical Trial Design: Many unsuccessful trials are not failures of the compound itself, but of inadequate formulation. Greater emphasis on pharmacokinetic assessment and the integration of advanced delivery technologies is essential to improve outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Variability in absorption—driven by factors such as gut microbiota composition, liver enzyme activity, and genetic differences—underscores the need for patient-specific dosing strategies rather than a one-size-fits-all model.
- Formulation Innovation: The use of nanocarriers, micelles, and lipid-based systems should be viewed as scientifically valid methods to enhance delivery and bioavailability, not as mere marketing tools.
- Regulatory Landscape: Regulatory bodies are placing increasing weight on pharmacokinetic evidence to substantiate therapeutic claims. Demonstrating systemic exposure and biological activity, rather than listing nominal doses, is becoming the standard for both pharmaceuticals and premium nutraceuticals.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of nutrients and bioactive compounds in cardiovascular, cognitive, and inflammatory health extends far beyond the milligram values listed on labels. True clinical benefit depends on bioavailability—the extent to which these compounds are absorbed, metabolized, and delivered to target tissues in concentrations sufficient to exert biological effects.
The mixed outcomes seen in trials of omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, polyphenols, and vitamin D underscore the limitations of milligram-based dosing alone. In contrast, progress in advanced delivery systems, formulation science, and personalized medicine demonstrates that improving bioavailability is key to consistent therapeutic results.
For healthcare and pharmaceutical professionals, this requires shifting the focus from dosage to functional delivery and tissue-level activity. Future research and clinical practice must emphasize optimized formulations, validated biomarkers, and individualized strategies. Only by moving beyond milligrams can we fully realize the potential of these compounds in protecting the heart, enhancing cognition, and regulating inflammation.
Other Articles You May Find of Interest...
- Relapsed/Refractory CLL/SLL: Interpreting Efficacy Endpoints Across Studies
- What Is the Kleihauer Betke Test and Why Is It Important for Maternal Health?
- Dr. Martin A. Schreiber to Present at STACS 2026 on Why Trauma Systems Fail First in Large Scale War
- ELISA Kits: Assay Formats, Detection Methods, & Data Interpretation
- Catherine O’Hara Cause of Death: What We Know — and What to Understand About Dextrocardia With Situs Inversus
- Texas Academy of Medical Aesthetics Sets New Standards for Clinical Excellence in Injector Training
- How Can Mouse CD14 Monoclonal Antibody Be Used In Immunoassays














